 Home-based businesses can be financially rewarding and provide a certain amount of flexibility with your day-to-day schedule. Here are some tips to keep your business running at full steam.
Home-based businesses can be financially rewarding and provide a certain amount of flexibility with your day-to-day schedule. Here are some tips to keep your business running at full steam.
- Stay on top of accounts receivable. It’s easy to get caught up with fulfilling your business obligations while invoices you’ve sent out go unpaid. Agree to payment terms in advance with new customers and immediately – but politely – communicate with them as soon as they miss a payment deadline. Keep current with regular invoicing and collections.
- Keep your bookkeeping records up-to-date. You may not realize you have an unpaid invoice that’s several months old unless your bookkeeping is up-to-date. Keeping accurate books involves more than balancing your bank accounts once a month. In addition to your monitoring your bank accounts, also consistently look at your accounts receivable, accounts payable, any debts (credit card, car loans or other borrowings), and all money you invest in your business. Ask for help if you don’t have enough time to do the bookkeeping yourself, or if you need help properly setting up your bookkeeping software.
- Check on permit requirements. Depending on what type of home-based business you have, you may be required to obtain various permits, licenses or other registrations. If you have not already done so, check with your town or city for local requirements. The Small Business Administration is also a good source to research information on permits.
- Get insured. Obtain adequate insurance for the type of operation you’ll be running. Besides the insurance required for business activities, you might consider adding a rider to your homeowner’s policy for liability protection should an accident occur on your property.
- Stay on top of technology. While you may not need a top of the line computer, be sure that the technology equipment you use can handle the bandwidth of everything you’ll ask it to do, including video calls, software apps and data storage. Also consider scheduling a time for your internet provider to visit your home to make sure everything is in working order and your security protocols are top notch. Have a back-up plan in place for when a device breaks down, including where you’ll go to have it repaired.
- Cash in on tax breaks. Take advantage of the tax breaks available to home-based businesses, including deductions for supplies, equipment and vehicle expenses. You may even be able to deduct the cost of your home office, including a pro-rated amount of your real estate taxes and utilities, if certain conditions are met.
- Set aside money to pay your taxes. Ask for help to calculate how much of your incoming cash you should be setting aside to pay your federal, state and local taxes. Consider opening a separate bank account to transfer your tax money into.
Know the way loans work…and use it to your advantage!
 Every banker knows that the majority of the money they make on a loan is made in the first few years of the loan. By understanding this fact, you can greatly reduce the amount you pay when buying your house, paying off your student loan, or buying a car. Here is what you need to know:
Every banker knows that the majority of the money they make on a loan is made in the first few years of the loan. By understanding this fact, you can greatly reduce the amount you pay when buying your house, paying off your student loan, or buying a car. Here is what you need to know:
Your payment never changes
When you obtain a loan, the components of that loan are interest, the number of years to repay the loan, the amount borrowed, and the monthly payment. Assuming a fixed rate note, the payment never changes. Here is an example of a $250,000 loan.
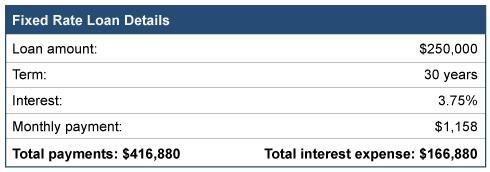
It is important to note that your payment in month one is $1,158 and your monthly payment thirty years later is the same amount…$1,158.
Each payment has two parts
What does change every month is what is inside each payment. Every loan payment has two parts. One is a payment that reduces the amount of money you owe, called principal. The other part of the payment is for the bank, called interest expense. Now look at the component parts of the first payment and then the last payment:

So, while your monthly payment never changes, the amount used to reduce the loan each month varies DRAMATICALLY. Remember your total cost of borrowing $250,000 includes more than $166,000 in interest!
Use the knowledge to your advantage
Here’s how you can use this information to your advantage.
For new loans
- Only sign up for loans that allow you to make pre-payments without penalty.
- When borrowing money, keep some of your cash in reserve. Try to reserve a minimum of 10 to 20 percent of the amount borrowed. So, in this example, try to reserve $25,000 to $50,000 in cash.
- Immediately after getting the loan, consider using the excess cash as a pre-payment on the note. By doing this you can dramatically reduce the interest expense over the life of the note, all while keeping your payment constant. Even though your monthly payment may be a little higher, the extra payment amount will pay back the loan more quickly.
For existing loans
- Create and look at your loan’s amortization table. This table shows how much of each payment is used to pay down the loan balance and how much goes to your lender as interest. In the above example, 67 percent of the first payment is for the bank, while only ½ of 1 percent of the last payment is for the bank.
- Pay more to you than the bank. Aggressively prepay down any loan until more of each payment goes to you versus the bank. This is the crossover point of your loan.
- Find your sweet spot. After hitting the crossover point, next consider the efficiency of each prepayment and determine when you consider your prepayment ineffective. No one would consider prepaying that last payment when interest expense is only $4.00. But if more than 25% of the payment goes to interest? Keep making prepayments.
Final thought
When you make a prepayment on a loan, reduce the loan balance by your prepayment, then look at the amortization table. See how many payments are eliminated with your prepayment and add up all the interest you save. You will be amazed by the result.
How to Shield Your Money From Inflation
 Recent high inflation rates are driving up the price for almost everything and eroding the value of your money. With varying opinions on the potential duration of the current inflation surge, it’s important to understand the causes and how you can protect your money.
Recent high inflation rates are driving up the price for almost everything and eroding the value of your money. With varying opinions on the potential duration of the current inflation surge, it’s important to understand the causes and how you can protect your money.
Possible causes of this inflation
While the root causes of inflation are not always easy to identify, the premise is simple – prices are going up for goods and services. This is often because demand is higher than supply. Here are some of the basic drivers of today’s inflation.
- The demand-pull situation. Demand for a product increases but the supply remains the same. Think of a vendor selling ponchos at a state fair. If it rains, demand is going to spike and fair-goers are willing to pay up to keep dry. This situation is rampant during the pandemic, as we all see runs on things like toilet paper and hand sanitizer. And now we are seeing pent-up demand being released, as some of the pandemic restrictions are eased. An example of this is popular vacation locations being all booked in advance.
- The cost-push situation. Demand stays constant but supply is reduced. An example of this is a lower-yield crop season when a major drought hits a region. Consumers still want their dinner salads, but lettuce is sparse. So, retailers charge more to cover their increased costs. Or when paper mills switched production to handle higher toilet paper demand, pulp used for paper and packaging had supply reductions creating a shortage which increased their prices.
- Factoring in the money supply. The more money there is available to spend (high money supply), the more the demand on all goods and services goes up. This is being manifested in wage increases as employers are having a hard time filling jobs and is also the result of many of the government spending programs during the pandemic.
Ideas to protect yourself during high inflation
- Alternative savings that is NOT cash. The value of your money sitting in your wallet or in low interest bank accounts is shrinking before your eyes. The past year has seen the highest inflation rates in the last decade at 5.4%, according to the Consumer Price Index (CPI). That means if your savings account is earning 0.6%, you’ve lost 4.8% in purchasing power over the last 12 months. Get your money to work for you by considering:
- Low risk, dividend-paying stocks
- CDs, bonds and other investments with various maturities to prepare for higher rates
- Direct lending vehicles through vetted, respected facilitators
- Investing directly in property, small businesses or other tangible assets
- Invest in yourself to learn a new trade or skill
- Lock in fixed rates on debt. Inflation can be your friend if you have a low interest, fixed-rate loan. For example, inflation will tend to increase the value of your house over time, yet your monthly payment will remain the same. So borrowing money at a low fixed interest rate, while the underlying property value increases with inflation, can be a strategy to consider.
- Delay large expenditures. Do your part to reduce demand by postponing large purchases. Consider delaying the purchase of a new car, adding to your home or taking an overseas trip until demand flattens and prices come back to a normal rate.
It’s impossible to avoid the effects of high inflation altogether, but with some smart investing and the will-power to temporarily curb spending, you can reduce inflation’s impact on your personal bottom line.
Knowing your net worth and understanding how it is changing over time is one of the most important financial concepts that everyone needs to understand. This number is used by banks, mortgage companies, insurance companies and you! Your net worth impacts your credit score, which in turn impacts your interest rates and things as mundane as the amount you pay for auto insurance.
A simple definition
- Net worth is the result of taking all the things you own (assets) minus what you owe others (debts and liabilities).
- Assets include cash, bank account balances, investments, your home, vehicles or anything else that you could sell today for cash. Assets also include any businesses or business interests you own.
- Liabilities are what you owe others, such as a mortgage or car loan, and any other debt, like credit card or student loan debt.
 Your net worth changes over time, reflecting how you spend your money. For example, if you have tons of bills and spend more than you bring in, your bank account balances will be lower. If you spend a lot on your credit cards, your debt will go up. The net effect is a lower net worth.
Your net worth changes over time, reflecting how you spend your money. For example, if you have tons of bills and spend more than you bring in, your bank account balances will be lower. If you spend a lot on your credit cards, your debt will go up. The net effect is a lower net worth.
Everyone has a net worth
Yes, everyone. Even a 6-year-old with money in their piggy bank has a net worth. If your child is saving up for a bike, they will convert one asset (cash) into another asset (their new bike)!
Calculating your net worth
- Step one. Reconcile your bank accounts and loans. Try doing this every month, as these are the easiest parts of your net worth to track and calculate.
- Step two. Calculate the value of all your remaining assets. For some of your assets, such as stocks, you can go online and find the current value of the stocks you own. For other assets, you’ll have to estimate what you could sell that asset for today.
- Step three. Add up all your asset values, then subtract all your debts. What you’re left with is your net worth (and yes, your number could be negative)!
Why you should know your net worth
Knowing your net worth contributes to the big picture of your financial circumstances. Here’s why it’s beneficial to know your net worth:
- You want to apply for student loans. You’ll likely need to submit an application that details all your cash and other assets when applying for student loans. If your net worth is high enough, you may have to foot some of the tuition bill yourself.
- You want to get insurance. Some types of insurance use your credit score as part of the calculation for determining your premium payments. Knowing if you have a high net worth may help in obtaining a favorable premium amount.
- You want to diversify your investments. Certain investments are available only to individuals who have a high enough net worth.
- You want to buy a home. Banks want to see that you have plenty of cash when compared to your debts. If you have too much debt, you may need to either pay down the debt or increase your down payment.
Knowing your net worth and how to calculate it can help you achieve some of your financial goals. Please call if you’d like help calculating and understanding your net worth.
When it comes to money topics, you’re always hearing how to save more. But even with the best of intentions, you can run into trouble when you try to save too much. Here are four ways that savings can get in your way and how you can correct them.
 Savings that turns into spending. Buying something on sale to save money is still spending. Focus on the amount of money you have to part with, instead of focusing on the great deal. These deals use the human emotion of the fear of losing out, causing you to spend money you did not plan on spending in the first place.
Savings that turns into spending. Buying something on sale to save money is still spending. Focus on the amount of money you have to part with, instead of focusing on the great deal. These deals use the human emotion of the fear of losing out, causing you to spend money you did not plan on spending in the first place.
What you can do: Plan your purchases. If something on your list of planned purchases is then on sale, you will truly be saving money. So instead of saving 50% on a new lawn mower, save 100% because you already have one that works just fine.
Savings that turns into hoarding. This could happen if you have a hard time parting with things for fear you might be able to use it in the future. This could be as simple as buying a new set of dishes or a new pair of shoes and hanging on to the old ones just in case. Each time you acquire something new without throwing out the old, your house gets stuffed with items you don’t need.
What you can do: When you need to replace something, try to sell the old item right after bringing in the new item(s). Not only will this keep the clutter out of your home, it will effectively lower the cost of the replacement. And periodically review the contents of your household. Have you used it in the last 12 months? If not, chances are good that you won’t need it in the foreseeable future.
Not replacing things when you should. This savings behavior might actually be costing you money. For example, that old water heater still works, but it could be so inefficient that it is costing a ton in excess electricity or gas. The same could be true with an old car’s maintenance bills or even wearing clothes even though you’ve worn holes in them.
What you can do: Consider replacements as investments. For instance, replacing the old brakes in your car is an investment in your safety. Replacing your worn out shoes is an investment in your comfort. Replacing your toothbrush that is falling apart is an investment in your health.
Risking damages or dangers. It’s great to save money by doing something by yourself, but know your limits. Sure, cutting down that old tree by yourself can save you a ton of money. But the emergency room is full of do-it-yourself savers who lack the experience to do it safely. The same can be true with making financial decisions or even wading through the tax code on your own.
What you can do: Know your limits and ask for help. Sometimes paying a little more is worth it if it means avoiding a potentially dangerous or financially negative situation.
Which unique method of budgeting will work for you?
 You have your own unique personality, preferences and lifestyle. Likewise, how you manage and organize your finances can have its own personality, including how you budget. Here are five different methods of budgeting, each with a distinct way of helping you organize your spending and finances.
You have your own unique personality, preferences and lifestyle. Likewise, how you manage and organize your finances can have its own personality, including how you budget. Here are five different methods of budgeting, each with a distinct way of helping you organize your spending and finances.
- Traditional budget. Use last year’s budget as a base, make any necessary adjustments due to changes in your income or expenses, and create your budget by taking your income minus your expenses to equal the amount you have to spend.
- Envelope budget. Keep a set amount of cash for the month in envelopes labeled with an expense category like groceries, clothing, eating out, entertainment, etc. Use one envelope per expense category. If you run out of money in one envelope, you can dip into other envelopes, but this will obviously impact spending in those areas.
- Reverse budget. Instead of stashing away the money left over after you’re done spending for the month, first take out your portion for savings and then spend the amount of money that remains. Reverse budgeting is an effective way to prioritize saving for your future retirement, an emergency or rainy-day fund, or other big expenses like a vacation, a new car, or a down payment on a house.
- Zero-based budget. Know where each dollar is going and record every single dollar spent. Also called the zero-sum or down-to-the-dollar budget, this method helps you get specific about spending and keeping track of all your dollars. Instead of one amount allotted for food, you know exactly how much you will spend on groceries, lunch while at work, and dining out. Instead of one amount allotted for savings, you know exactly how much you are putting into retirement, loan repayment, and emergency savings.
- 50/20/30 budget. Stick to three spending categories. Each month, 50% of your take-home income goes toward needs, 20% toward savings, and 30% toward wants. Examples of needs are housing or car payments and groceries. Savings could be retirement money, paying off loans, and emergency funds. Wants include things like shopping, vacation, or entertainment. Less detailed than the zero-based or envelope methods but more detailed than traditional or reverse budgeting, the 50/20/30 method helps you monitor money habits by helping you stick to three categories every month.
The best budget approach? One that works for you and one that you will continue to use. So pick an approach and try it. It can really change how you spend your money.
As always, should you have any questions or concerns regarding your tax situation please feel free to call.
Banking tips to help you cash in
Your cash is parked. Do you know if it’s making or losing you money? For instance, letting it sit in a non-interest-bearing account is a waste of earnings potential. It’s actually losing money if you factor in inflation! Here are some ideas to help you make the most of your banked cash:
Understand your bank accounts. Not all bank accounts are created equal. Interest rates, monthly fees, minimum balances, direct deposit requirements, access to ATMs, other fees and customer service all vary from bank to bank and need to be considered. Start by digging into the details of your accounts. There may be some things you’ve been unnecessarily living with like ATM fees or monthly account charges. Once you have a handle on your current bank, conduct research on what other banks have to offer.
Know your interest rates. As a general rule, the more liquid an account, the lower the interest rate. Checking accounts offer the lowest rates, then savings accounts, which yield lower rates than CDs. Maximizing your earnings is as simple as keeping your cash in accounts with higher interest rates. The overall interest rate earned between all your accounts should be higher than the inflation rate, which is generally around 2 percent.
Make smart moves. There are a couple of things to take into account when making transfers. First, federal law allows for only six transfers from savings and money market accounts per month. Second, if you invest in longer term investments like CDs or bonds, there are penalties for withdrawing funds before the maturity date. So make sure you can live without the funds for the duration of the term.
Stay diligent. Putting together a cash plan is just the start. The key to success is to be persistent. Besides losing out on potential earnings, mismanaging your cash can result in hefty overdraft fees. The more attention you devote, the more your money will grow.
 As the end of the year approaches, there is still time to make moves to manage your tax liability. Here are some ideas to consider.
As the end of the year approaches, there is still time to make moves to manage your tax liability. Here are some ideas to consider.
Maximize your retirement plan contributions. This includes traditional IRAs, Roth IRAs, and SEP IRAs for self-employed. Now is the time to maximize the contribution potential for this year and plan for next year’s contributions.
Estimate your current and next year taxable income. With this estimate you can determine which year receives the greatest benefit from a reduction in income. By understanding what the tax rate will be for your next dollar earned, you can understand the tax benefit of reducing income in this year versus next year.
Make charitable contributions. Consider which tax year will benefit most from your charitable giving of cash and non-cash items. Shift your giving into the year that will provide you the most benefit.
Take capital losses. Each year you can net capital losses against capital gains. You can also deduct up to $3,000 in excess losses against your other income. Start to identify which investments may make sense to sell to take advantage of this. If planned correctly, these losses can offset ordinary income.
Consider donating appreciated stock. This strategy gives you a charitable deduction for the market value of the stock, while not having to pay capital gains tax on the charitable gift. If you provide an annual pledge sheet to your church, this can be a great way to maximize your gift while giving needed funds to your church at the beginning of the year.
Retirement plan distributions. If you are age 70½ or older, take your required minimum distributions for the year. If you are retired, but younger than 70½, consider taking tax efficient distributions from your retirement accounts. By paying some tax now, you may avoid paying higher taxes later when you have to follow the minimum distribution rules.
Consider tax legislation. Please recall that tax laws passed in late 2016 made many temporary tax savings permanent and extended others into 2017. So save classroom related receipts if you are a teacher. Consider charitable contributions from your retirement plan if you are a senior. Keep receipts of large purchases to track a potential sales tax deduction.