Meals Continue To Be Deductible Under New IRS Guidance
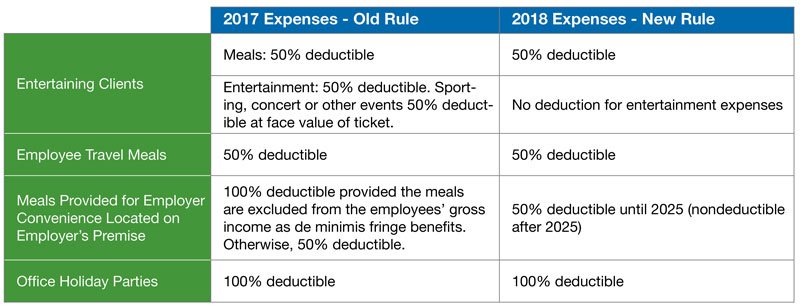
The IRS issued guidance clarifying that taxpayers may generally continue to deduct 50% of the food and beverage expenses associated with operating their trade or business, despite changes to the meal and entertainment expense deduction made by the tax law known as the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA). According to the IRS, the amendments specifically deny deductions for expenses for entertainment, amusement, or recreation, but do not address the deductibility of expenses for business meals. This omission has created a lot of confusion in the business community, which the IRS is addressing in this interim guidance. Taxpayers can rely on the guidance in the notice until the IRS issues proposed regulations.
Sec. 274(k), which was not amended by the TCJA, does not allow a deduction for the expense of any food or beverages unless (1) the expense is not lavish or extravagant under the circumstances, and (2) the taxpayer (or an employee of the taxpayer) is present when the food or beverages are furnished. Sec. 274(n)(1), which was amended by the TCJA, generally provides that the amount allowable as a deduction for any expense for food or beverages cannot exceed 50% of the amount of the expense that otherwise would be allowable.
Under the interim guidance, taxpayers may deduct 50% of an otherwise allowable business meal expense if:
- The expense is an ordinary and necessary business expense under Sec. 162(a) paid or incurred during the tax year when carrying on any trade or business;
- The expense is not lavish or extravagant under the circumstances;
- The taxpayer, or an employee of the taxpayer, is present when the food or beverages are furnished;
- The food and beverages are provided to a current or potential business customer, client, consultant, or similar business contact; and
- For food and beverages provided during or at an entertainment activity, they are purchased separately from the entertainment, or the cost of the food and beverages is stated separately from the cost of the entertainment on one or more bills, invoices, or receipts.
The IRS will not allow the entertainment disallowance rule to be circumvented through inflating the amount charged for food and beverages.
The notice contains three examples illustrating how the IRS intends to interpret these rules. All three examples involve attending a sporting event with a business client and having food and drink while attending the game. The examples follow the AICPA’s recommendation that meal expenses be deductible when their costs are separately stated from the cost of the entertainment.
- The IRS plans to issue proposed regulations and is requesting comments by Dec. 2 on the notice. It is also asking for comments on:Whether further guidance is needed to clarify the interaction of Sec. 274(a)(1)(A) entertainment expenses and business meal expenses.
- Whether the definition of entertainment in Regs. Sec. 1.274-2(b)(1)(i) should be retained and, if so, whether it should be revised.
- Whether the objective test in Regs. Sec. 1.274-2(b)(1)(ii) should be retained and, if so, whether it should be revised.
- Whether the IRS should provide more examples in the regulations.
In a letter to the IRS dated April 2, 2018, the AICPA had requested that the IRS provide immediate guidance on the TCJA change to Sec. 274. The AICPA recommended that the IRS confirm that business meals (1) that take place between a business owner or employee and a current or prospective client; (2) that are not lavish or extravagant under the circumstances; and (3) where the taxpayer has a reasonable expectation of deriving income or other specific trade or business benefit from the encounter are deductible.

