Know the way loans work…and use it to your advantage!
 Every banker knows that the majority of the money they make on a loan is made in the first few years of the loan. By understanding this fact, you can greatly reduce the amount you pay when buying your house, paying off your student loan, or buying a car. Here is what you need to know:
Every banker knows that the majority of the money they make on a loan is made in the first few years of the loan. By understanding this fact, you can greatly reduce the amount you pay when buying your house, paying off your student loan, or buying a car. Here is what you need to know:
Your payment never changes
When you obtain a loan, the components of that loan are interest, the number of years to repay the loan, the amount borrowed, and the monthly payment. Assuming a fixed rate note, the payment never changes. Here is an example of a $250,000 loan.
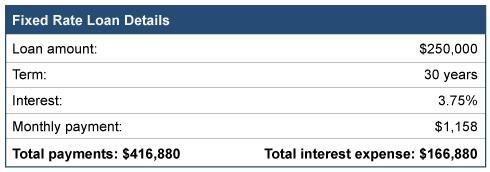
It is important to note that your payment in month one is $1,158 and your monthly payment thirty years later is the same amount…$1,158.
Each payment has two parts
What does change every month is what is inside each payment. Every loan payment has two parts. One is a payment that reduces the amount of money you owe, called principal. The other part of the payment is for the bank, called interest expense. Now look at the component parts of the first payment and then the last payment:

So, while your monthly payment never changes, the amount used to reduce the loan each month varies DRAMATICALLY. Remember your total cost of borrowing $250,000 includes more than $166,000 in interest!
Use the knowledge to your advantage
Here’s how you can use this information to your advantage.
For new loans
- Only sign up for loans that allow you to make pre-payments without penalty.
- When borrowing money, keep some of your cash in reserve. Try to reserve a minimum of 10 to 20 percent of the amount borrowed. So, in this example, try to reserve $25,000 to $50,000 in cash.
- Immediately after getting the loan, consider using the excess cash as a pre-payment on the note. By doing this you can dramatically reduce the interest expense over the life of the note, all while keeping your payment constant. Even though your monthly payment may be a little higher, the extra payment amount will pay back the loan more quickly.
For existing loans
- Create and look at your loan’s amortization table. This table shows how much of each payment is used to pay down the loan balance and how much goes to your lender as interest. In the above example, 67 percent of the first payment is for the bank, while only ½ of 1 percent of the last payment is for the bank.
- Pay more to you than the bank. Aggressively prepay down any loan until more of each payment goes to you versus the bank. This is the crossover point of your loan.
- Find your sweet spot. After hitting the crossover point, next consider the efficiency of each prepayment and determine when you consider your prepayment ineffective. No one would consider prepaying that last payment when interest expense is only $4.00. But if more than 25% of the payment goes to interest? Keep making prepayments.
Final thought
When you make a prepayment on a loan, reduce the loan balance by your prepayment, then look at the amortization table. See how many payments are eliminated with your prepayment and add up all the interest you save. You will be amazed by the result.

 According to the Federal Reserve, U.S. student loan debt is now $1.5 trillion with more than 44 million borrowers. Only mortgage debt currently has bigger numbers among types of consumer debt. Even worse, more than 10 percent of these loans are past due. Here are some tactics to help make student debt easier to manage:
According to the Federal Reserve, U.S. student loan debt is now $1.5 trillion with more than 44 million borrowers. Only mortgage debt currently has bigger numbers among types of consumer debt. Even worse, more than 10 percent of these loans are past due. Here are some tactics to help make student debt easier to manage: Make tax-wise investment decisions. Have some loser stocks you were hoping would rebound? If the prospects for revival aren’t great, and you’ve owned them for less than one year (short-term), selling them now before they change to long-term stocks can offset up to $3,000 in ordinary income this year. Conversely, appreciated stocks held longer than one year may be candidates for potential charitable contributions or possible choices to optimize your taxes with proper planning.
Make tax-wise investment decisions. Have some loser stocks you were hoping would rebound? If the prospects for revival aren’t great, and you’ve owned them for less than one year (short-term), selling them now before they change to long-term stocks can offset up to $3,000 in ordinary income this year. Conversely, appreciated stocks held longer than one year may be candidates for potential charitable contributions or possible choices to optimize your taxes with proper planning.